Tooth loss and gum disease are common oral health concerns that can, if left untreated, compromise the integrity of a patient’s mouth and oral structures. Bone grafting can help restore the foundation of a patient’s jaw, providing a higher chance of success during dental implant procedures. Our implant dentist, Dr. Donian Shen, is dedicated to providing patients with beautiful, secure smiles using the most effective and advanced treatments available.
- What Is Bone Grafting?
- Bone Graft Types
- When Is Bone Grafting Needed?
- Bone Grafting Procedure
- Bone Grafting Recovery
What Is Bone Grafting?
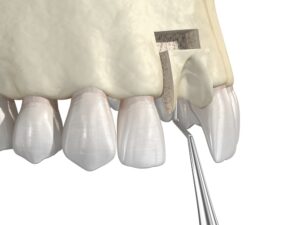 Bone grafting is a procedure designed to restore the structural integrity of a patient’s jaw, thus making it possible for dental implants and implant-supported dentures to be successfully placed. Also known as pre-prosthetic surgery, bone grafting increases bone mass in areas where it has been depleted, most commonly as a result of gum disease and/or tooth loss. The procedure can be performed several different ways, depending on a patient’s needs. Dr. Shen will perform a thorough assessment of your jaw, gums, and oral structures in order to determine the optimal approach.
Bone grafting is a procedure designed to restore the structural integrity of a patient’s jaw, thus making it possible for dental implants and implant-supported dentures to be successfully placed. Also known as pre-prosthetic surgery, bone grafting increases bone mass in areas where it has been depleted, most commonly as a result of gum disease and/or tooth loss. The procedure can be performed several different ways, depending on a patient’s needs. Dr. Shen will perform a thorough assessment of your jaw, gums, and oral structures in order to determine the optimal approach.
What Are the Different Types of Bone Grafts?
Typical bone graft types used to repair the jawbone include:
- Autograft — Autograft bone tissue is taken from elsewhere on the patient’s body, such as the chin or hip.
- Allograft – Allograft bone tissue is voluntarily harvested from a previously healthy, but now deceased, human donor.
- Xenograft (animal tissue) – Xenograft bone tissue is taken from an animal, such as a pig or cow, that has a similar bone composition to humans.
When Is Bone Grafting Needed?
Bone grafting is needed when there is inadequate jawbone density to properly support a dental implant. If there is not enough bone for the implant post to fuse to, the implant procedure has a much lower chance of being successful.
In addition to creating a better foundation for dental implant restorations, bone grafting can also enhance speaking and eating function while protecting the integrity of a patient’s facial features and oral structures.
How Is the Bone Grafting Procedure Performed?
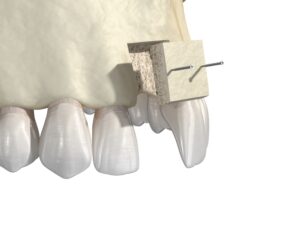 The bone grafting procedure begins with local anesthesia being applied to the grafting site. Depending on a patient’s treatment plan and individual needs, sedation dentistry techniques can also be employed to make the experience as comfortable and relaxed as possible.
The bone grafting procedure begins with local anesthesia being applied to the grafting site. Depending on a patient’s treatment plan and individual needs, sedation dentistry techniques can also be employed to make the experience as comfortable and relaxed as possible.
Once the patient is properly numbed—and sedated, as needed—the bone tissue will be prepared. A small incision is made in the gums so that your dentist can access the jawbone. From there, the bone graft material is placed and the incision is then closed. In many cases, a protective membrane may be used to help secure the bone graft material in place.
How Long Does a Bone Graft Take to Heal?
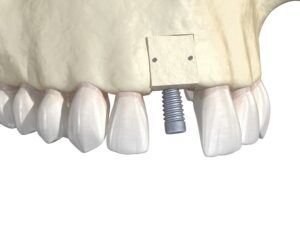 Although precise timelines can vary between patients, most bone grafts take around six to nine months to fully heal, at which point you can proceed with dental implant surgery. With bone grafting typically being an outpatient procedure, patients should be able to return home the same day to begin the recovery process. Most patients report that any swelling or discomfort around the incision site is typically well-managed with over the counter pain medication.
Although precise timelines can vary between patients, most bone grafts take around six to nine months to fully heal, at which point you can proceed with dental implant surgery. With bone grafting typically being an outpatient procedure, patients should be able to return home the same day to begin the recovery process. Most patients report that any swelling or discomfort around the incision site is typically well-managed with over the counter pain medication.
For more information on bone grafting, contact our office to schedule a consultation.




